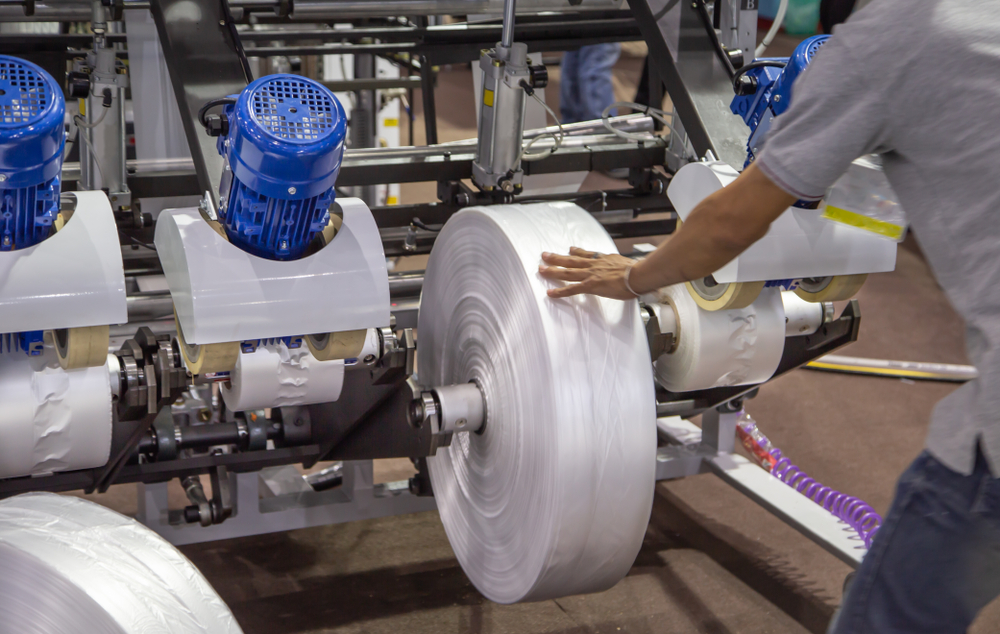
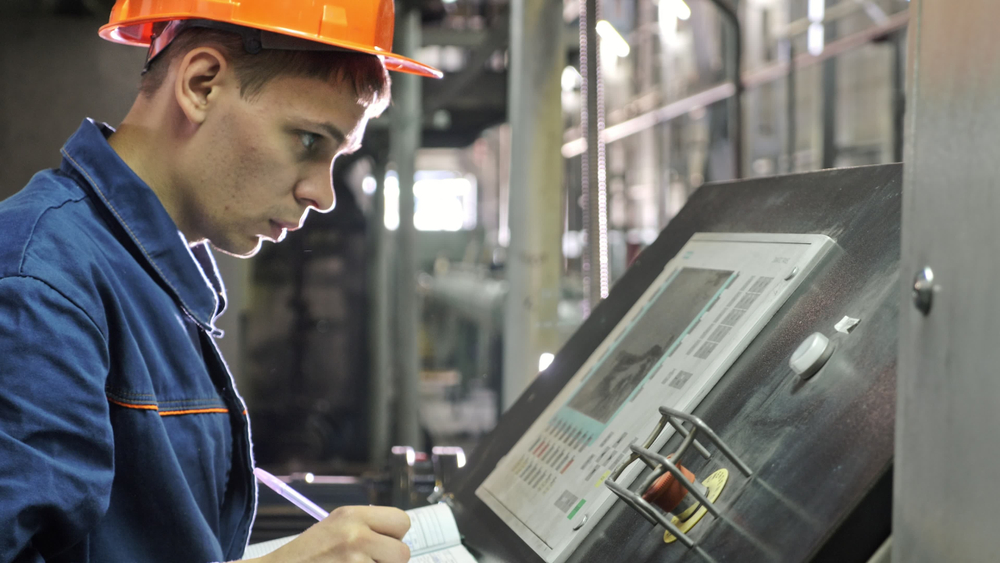
An Extrusion Machine Operator is a skilled technician responsible for operating and maintaining machinery that shapes materials by forcing them through a die. This process is widely used in manufacturing industries, including plastics, metals, and food production, to create products with a consistent cross-sectional profile. The operator’s role is crucial in ensuring the efficient and accurate production of items such as pipes, sheets, films, and profiles.
Responsibilities of an Extrusion Machine Operator
Extrusion Machine Operators have a range of responsibilities that ensure the smooth operation of the extrusion process:
- Machine Setup: Setting up extrusion machines according to specific job requirements, which includes selecting and installing dies, configuring machine controls, and adjusting temperatures and pressures.
- Operation Monitoring: Continuously monitoring the extrusion process to ensure materials are being shaped correctly and to specification. This involves adjusting controls to maintain the quality and consistency of the output.
- Quality Control: Inspecting extruded products for defects and making necessary adjustments to the machine settings. Operators must be adept at detecting and correcting issues to maintain high-quality standards.
- Routine Maintenance: Conducting routine maintenance tasks such as cleaning, lubricating, and performing minor repairs on the machinery to prevent breakdowns and ensure longevity.
- Record Keeping: Maintaining accurate records of production data, machine settings, and maintenance activities. This documentation is essential for tracking performance and troubleshooting issues.
Educational Pathways
High School Education
The foundational requirement for becoming an Extrusion Machine Operator is a high school diploma or GED. High school courses in mathematics, physics, and shop classes can provide a useful background for understanding the principles of extrusion and machine operation.
Vocational and Technical Training
While some Extrusion Machine Operators learn on the job, enrolling in a vocational or technical training program can provide a significant advantage. Programs in manufacturing technology, plastics technology, or mechanical engineering often include coursework relevant to extrusion processes, such as:
- Basic principles of extrusion
- Material science and properties
- Blueprint reading and technical drawing
- Machine operation and maintenance
Certification
Certifications, though not always required, can enhance an operator’s credentials and job prospects. Organizations like the Society of Plastics Engineers (SPE) offer certifications that demonstrate a candidate’s proficiency and commitment to the industry. Certification typically involves completing coursework and passing an examination.
Skills and Qualities of a Successful Extrusion Machine Operator
- Technical Proficiency: Operators must understand the mechanical and thermal dynamics of the extrusion process, as well as how to troubleshoot and maintain machinery.
- Attention to Detail: Precision is critical in extrusion. Operators must carefully monitor and adjust machine settings to ensure products meet exact specifications.
- Problem-Solving Skills: The ability to quickly diagnose and fix issues that arise during the extrusion process is essential for maintaining productivity and quality.
- Physical Stamina and Strength: Operators often handle heavy materials and equipment, requiring physical endurance and strength.
- Safety Consciousness: Adhering to safety protocols is vital to prevent accidents and injuries. Operators must be vigilant and proactive in maintaining a safe work environment.
Steps to Become an Extrusion Machine Operator
- Complete High School or Equivalent: Obtain a high school diploma or GED, focusing on relevant subjects like math and physics.
- Pursue Technical Education: Enroll in a vocational training program related to manufacturing technology or plastics technology.
- Gain Hands-On Experience: Start with entry-level positions in manufacturing to gain practical experience. Apprenticeships or on-the-job training programs can provide structured learning opportunities.
- Obtain Certification: Consider obtaining certification from recognized industry organizations to enhance your qualifications.
- Seek Employment: Apply for positions as an Extrusion Machine Operator in various industries such as plastics manufacturing, metals processing, or food production.
- Continue Learning: Stay updated with the latest technologies and practices in extrusion. Continuous education and training can lead to career advancement.
Career Outlook and Advancement
The demand for Extrusion Machine Operators is stable, reflecting the broad application of extrusion processes across multiple industries. According to industry data, employment opportunities in this field are expected to grow steadily, with particularly strong prospects for those who have formal training and certifications.
Experienced operators can advance to supervisory roles, oversee production lines, or move into specialized areas such as process engineering or quality control. Further education and training can open up additional career paths, including roles in management or technical sales.
Salary Expectations
Salaries for Extrusion Machine Operators vary based on factors such as experience, location, and industry. On average, entry-level operators can expect to earn between $30,000 and $40,000 annually, while experienced operators can earn from $40,000 to $60,000. Additional factors such as overtime, shift differentials, and specialized skills can also impact earnings.
Challenges and Rewards
Challenges: The role of an Extrusion Machine Operator can be physically demanding and requires a high level of precision and concentration. Operators must be prepared to work in environments that may be noisy and require adherence to strict safety protocols.
Rewards: Despite the challenges, the role offers significant rewards, including the satisfaction of creating essential products used in various industries. The career also provides opportunities for continuous learning and advancement, making it a dynamic and fulfilling profession.
The Role of Technology in Extrusion
Advanced Machinery: Technological advancements have significantly impacted the extrusion process. Modern extrusion machines are equipped with advanced control systems that allow for precise adjustments and monitoring. These technologies enhance the efficiency and quality of the extrusion process, making it crucial for operators to stay updated with the latest machinery and software.
Automation: The integration of automation in extrusion processes has increased productivity and consistency. Automated systems can handle repetitive tasks, allowing operators to focus on more complex aspects of production. Familiarity with automation technologies is becoming increasingly important for Extrusion Machine Operators.
Sustainability: The push towards more sustainable manufacturing practices has also influenced the extrusion industry. Operators are now expected to optimize material usage and minimize waste. Techniques such as lean manufacturing and Six Sigma are being applied to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact.
Work Environment and Safety Standards
Work Environment: Extrusion Machine Operators typically work in manufacturing plants, which can be noisy and bustling. These environments are designed to maximize productivity and safety. Operators may work in shifts, including nights and weekends, depending on the company’s production needs.
Safety Standards: Safety is paramount in the extrusion industry. Operators must adhere to strict safety protocols to prevent accidents and injuries. This includes wearing protective gear, following proper procedures for machine operation, and conducting regular safety checks. A safe work environment not only protects operators but also ensures consistent production without costly interruptions.
Professional Development and Continuing Education
Continuous Learning: In a technically demanding field like extrusion, professional growth is often linked to an operator’s willingness to learn and adapt. Continuous education can take various forms, from formal coursework to attending industry seminars and workshops. These opportunities enhance an operator’s skills and broaden their understanding of the industry.
Further Education: Operators interested in advancing their careers can pursue further education in fields such as mechanical engineering, industrial technology, or business management. These qualifications can prepare operators for roles in management, operations planning, or even starting their own manufacturing business. Community colleges and technical schools often offer courses specifically designed to upgrade the skills of manufacturing personnel.
Real-World Applications of Extrusion
Plastics Industry: The plastics industry is one of the largest users of extrusion processes. Extrusion Machine Operators in this sector produce a wide range of products, including pipes, sheets, films, and profiles. The versatility of plastics and the precision of extrusion make this a vital industry for operators.
Metals Processing: Extrusion is also used in metals processing to create components for various applications, from construction to aerospace. Operators in this industry work with materials like aluminum and copper, requiring specialized knowledge and techniques.
Food Production: In the food industry, extrusion processes are used to create products such as pasta, cereals, and snacks. Operators must understand the unique properties of food materials and ensure that products meet health and safety standards.
Tips for Success as an Extrusion Machine Operator
Develop a Keen Eye for Detail: Success as an Extrusion Machine Operator hinges on attention to detail. Operators must carefully inspect each product for accuracy and quality, identifying any defects or deviations from specifications.
Effective Communication Skills: Strong communication skills are essential for Extrusion Machine Operators, who often work as part of a larger production team. Effective communication with supervisors, engineers, and other team members ensures that any issues are promptly addressed and that the production process runs smoothly.
Embrace a Safety-First Mindset: A safety-first mindset is critical in this profession. Operators should be proactive in identifying potential hazards and committed to following all safety protocols. Regularly attending safety training sessions and staying updated on best practices can help operators maintain a safe working environment.
Continuous Improvement: Adopting a mindset of continuous improvement can significantly enhance an operator’s career prospects. This involves regularly seeking out new learning opportunities, whether through formal education, on-the-job training, or self-study. Staying abreast of industry trends and innovations ensures that operators remain valuable assets to their employers and can advance in their careers.
Becoming an Extrusion Machine Operator offers a viable career path for those interested in a technical and hands-on profession. With opportunities for advancement and the need for skilled operators in various industries, it can be a fulfilling and stable career choice. By understanding the responsibilities, pursuing the necessary education and training, and continuously striving for improvement, individuals can thrive in this dynamic field.
FAQs
Do I need a college degree to become an Extrusion Machine Operator?
No, a college degree is not required. However, completing vocational training or an associate’s degree in a related field can be beneficial.
What industries employ Extrusion Machine Operators?
Extrusion Machine Operators are employed in various industries, including plastics manufacturing, metals processing, and food production.
How long does it take to become proficient as an Extrusion Machine Operator?
It typically takes a few months to a year of on-the-job training or an apprenticeship to become proficient.
Are there opportunities for advancement in this career?
Yes, experienced operators can advance to supervisory roles, quality control, or specialized technical positions.
What is the job outlook for Extrusion Machine Operators?
The job outlook is stable, with steady growth expected. Skilled operators, especially those with certifications, will have the best job prospects.
What does an aluminum extruder do?
The production of a broad variety of unique metal shapes can be accomplished in a cost-effective manner through the use of aluminum extrusion. Heating aluminum and then forcing it through a die in order to make extrusions is the technique that is being described here. Despite the fact that the fundamental technique is simple, the procedure is incredibly complicated in terms of the variety of shapes that may be generated with it.
What is an aluminum extrusion press operator job description?
This role is functionally responsible for reporting to the Extrusion Team Lead and is accountable for operating the press, process equipment, handling equipment, and die setup in a manner that is both safe and efficient. Maintaining a safe and secure working environment at all times is a requirement of the role, which requires adherence to the policies and procedures of the firm.
What does a plastic extruder operator do?
Becoming a plastic extrusion operator is one of the most popular career choices. In this role, you will oversee and manage the machinery that molds thermoplastic metals. This field significantly impacts our economy, often more profoundly than is widely acknowledged.
What does a plastic extrusion engineer do?
One of the roles that you will be responsible for in this capacity is providing assistance to production and engineering by establishing and operating extrusion equipment and procedures. It is also possible that you will be tasked with the responsibility of designing, establishing, and troubleshooting new methodologies and equipment for development.
What is the difference between plastic injection and plastic extrusion?
In essence, the extrusion process is essential for creating continuous, linear, two-dimensional shapes. On the other hand, injection molding is used to produce three-dimensional shapes that do not maintain a consistent parallel alignment.
What does rubber extruder do?
What is the difference between extruded and molded rubber?
This process is capable of creating three-dimensional shapes, which makes it perfectly suited for fabricating complex components used in various mechanical assemblies. Conversely, rubber extrusion generates two-dimensional parts in continuous lengths, designed to be cut according to the specific requirements of the application.